The recent buzz around artificial intelligence has largely revolved around its remarkable ability to generate captivating digital content from simple prompts. Alongside this excitement, however, come concerns about AI’s potential to disrupt the workforce and propagate convincing malicious propaganda. But amidst all this, one of AI’s most promising and perhaps less ominous applications is in the field of medicine. A recent update to Google’s AlphaFold software holds the promise of significant advancements in disease research and treatment.
Developed by Google DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs (also owned by Alphabet), AlphaFold has already showcased its ability to accurately predict how proteins fold. With a database of over 200 million known proteins, AlphaFold has been instrumental in various scientific discoveries, including advancements in malaria vaccines, cancer treatment, and enzyme designs.
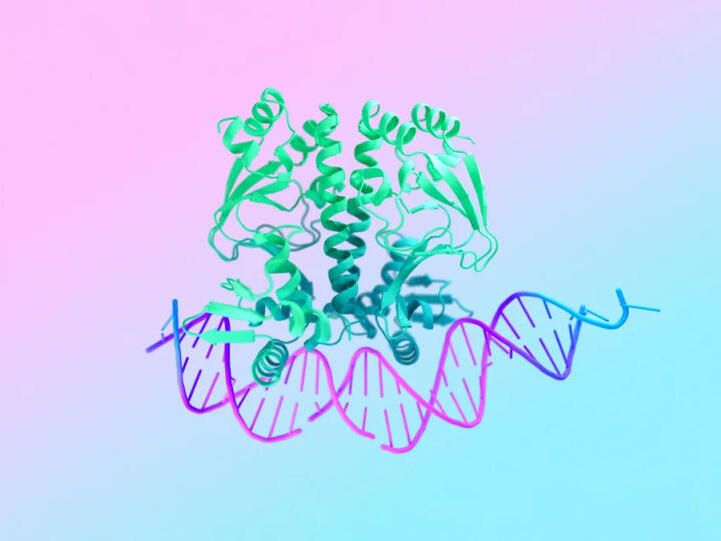
Understanding the shape and structure of proteins is crucial for developing new drugs or improving existing ones. The latest version, AlphaFold 3, goes beyond proteins to model other vital molecules, including DNA. It can also analyze interactions between drugs and diseases, potentially paving the way for groundbreaking research. Google claims that AlphaFold 3 achieves this with 50 percent better accuracy than existing models.
“AlphaFold 3 takes us beyond proteins to a broad spectrum of biomolecules,” wrote Google’s DeepMind research team. “This leap could unlock more transformative science, from developing biorenewable materials and more resilient crops to accelerating drug design and genomics research.”
Before the advent of AI, studying protein structures was a complex process involving electron microscopes and methods like X-ray crystallography. Machine learning simplifies this process by predicting protein shapes based on their amino acids.
AlphaFold 3’s improvements come from incorporating diffusion models into its molecular predictions. These models, commonly used in AI image generators, enhance the clarity of molecular structures by making educated guesses based on patterns from training data.
Google is offering AlphaFold 3 free for non-commercial research but has chosen not to open-source the project, a decision that disappointed some researchers. However, the software’s capabilities have impressed many in the scientific community.
Looking ahead, Google and Isomorphic Labs are collaborating with pharmaceutical companies to apply AlphaFold 3 to real-world drug design challenges, aiming to develop life-changing treatments for patients.